How Does Nozzle Affect Thrust
How Does Nozzle Affect Thrust, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
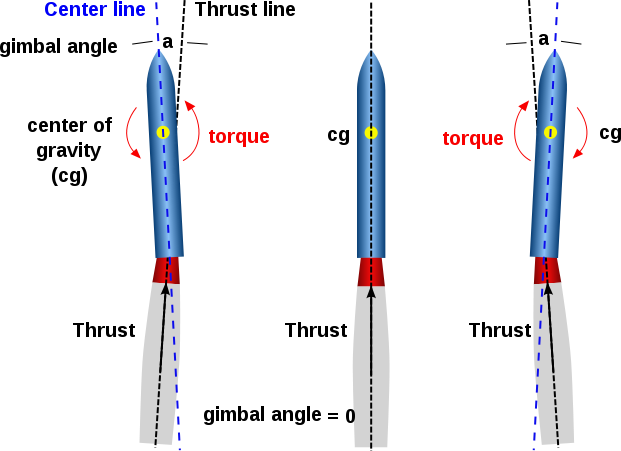
A rocket engine uses a nozzle to accelerate hot exhaust to produce thrust as described by newtons third law of motion.

Hydrant steamer nozzle. Large nozzle area ratios reduce engine efficiency at sea level. This reduction in efficiency occurs because the gas in the outermost areas around the nozzle expands to the point that its pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure which generates negative thrust. This flow behavior is also inefficient since some thrust force goes outward from the rocket instead of going in the opposite direction of the rocket flight.
Gas turbine engine operates under varying condition that affect the amount of thrust the engine produces. If the pressure is different it gets matched outside the engine where it doesnt produce thrust. With the increased temperature of the exhaust the flow area of the nozzle has to be increased to pass the same mass flow.
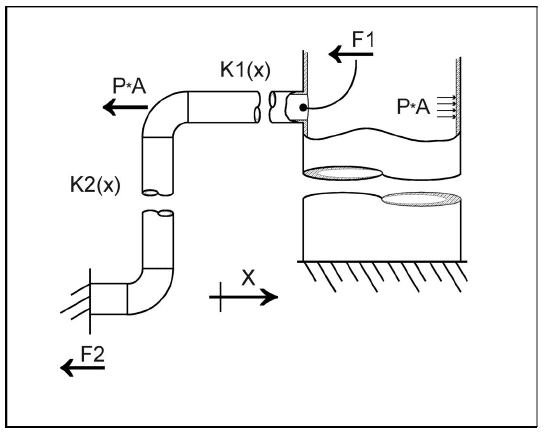
The amount of thrust produced by the engine depends on the mass flow rate through the engine the exit velocity of the flow and the pressure at the exit of the engine. The fuel burns and produces additional thrust but it doesnt burn as efficiently as it does in the combustion section of the turbojet. You get more thrust but you burn much more fuel.
When the engine is a rocket which creates high pressure the nozzle needs to expand the gas converting pressure to thrust through acting on the nozzle. Things to notice the maximum thrust is produced by the original spacex nozzle. The value of these three flow variables are all determined by the rocket nozzle design.
In general the job of a nozzle is to match the pressure at jet engine exit to that outside it. Since the gas coming from the exit nozzle is at a higher pressure than the surrounding gas the gas coming from the nozzle will expand outward as soon as it leaves the nozzle. Any exit area other than the original produces less thrust.