Rocket Nozzle Angle
Rocket Nozzle Angle, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
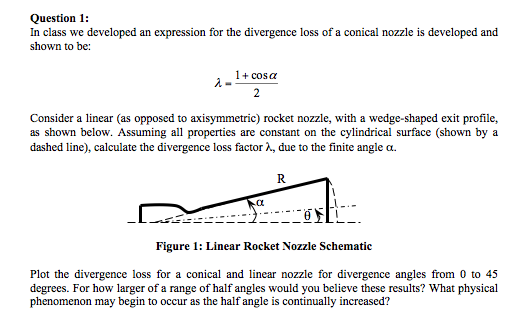
Equation 36 demonstrates that for a minimum length nozzle the expansion angle of the wall downstream of the throat is equal to one half the prandtl meyer function for the design exit mach number.

Ender 3 pro 02mm nozzle. The 60 degree half angle cone is shallower and is used to keep the overall length of the nozzle shorter. A rocket engine uses a nozzle to accelerate hot exhaust to produce thrust as described by newtons third law of motion. Since the gas coming from the exit nozzle is at a higher pressure than the surrounding gas the gas coming from the nozzle will expand outward as soon as it leaves the nozzle.
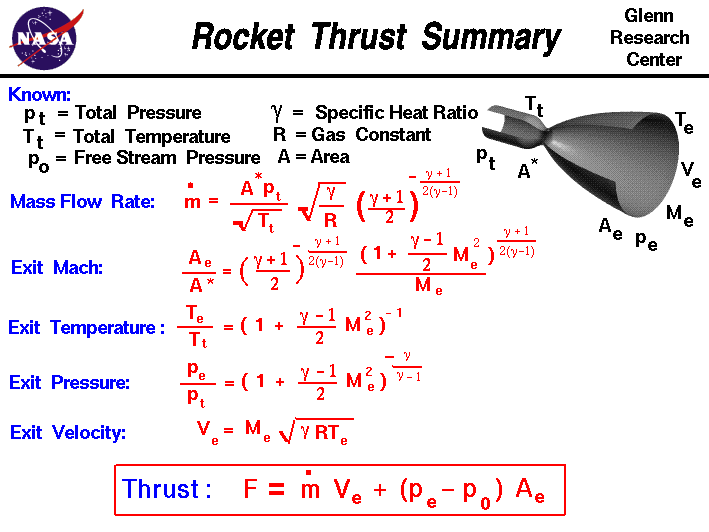
The value of these three flow variables are all determined by the rocket nozzle design. Ae6450 rocket propulsion altitudeambient pressure adjustment can use variable expansion ratio nozzles extendable two step nozzles eg rl 10b 2 on delta iv 2nd stage plugaerospike and ed nozzles requires full aerodynamic model to help determine nozzle boundaries plug. Ideally we would want to operate a rocket nozzle at the design condition but as the atmospheric pressure changes throughout a flight into space a rocket nozzle is typically overexpanded at take off and underexpanded in space.
Since the thrust no longer passes through the center of gravity a torque is generated about the center of gravity and the nose of the rocket turns to the left. To account for this variable area. Most also have a convergent or entrance cone with either a 45 degree half angle or a 60 degree half angle.
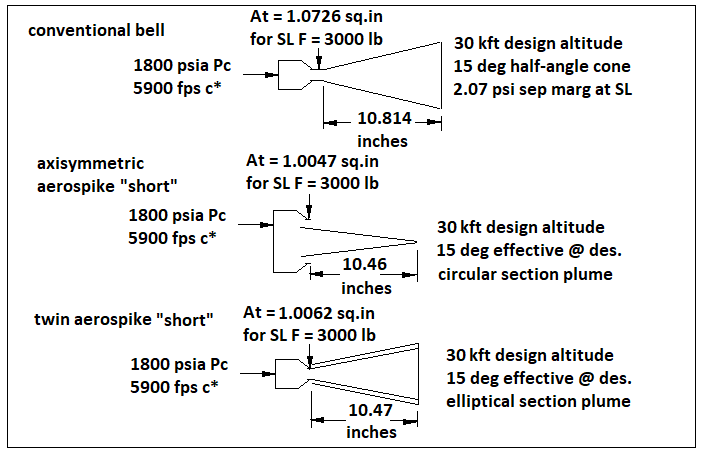
A small angle produces greater thrust because it maximizes the axial component of exit velocity and. The bell shaped or contour nozzle is probably the most commonly used shaped rocket engine nozzle. The conical nozzle was used often in early rocket applications because of its simplicity and ease of construction.
The amount of thrust produced by the engine depends on the mass flow rate through the engine the exit velocity of the flow and the pressure at the exit of the engine. This takes the rocket nozzle towards its optimum design condition as shown here. Smaller angles give very slightly higher efficiency larger angles give lower efficiency.
More complex shapes of revolution are frequently used such as bell nozzles or parabolic shapes. The half angle of this cone is known as the mach angle and is equal to. This is followed by a gradual reversal of nozzle contour slope so that at the nozzle exit the divergence angle is small usually less than a 10 degree half angle.
For case g what happens if we further reduce the exit pressure of the nozzle. The simplest nozzle shape has a 150 cone half angle which is about 98 efficient. Outer boundary ed.
It has a high angle expansion section 20 to 50 degrees right behind the nozzle throat.