Rocket Nozzle Heat Transfer
Rocket Nozzle Heat Transfer, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
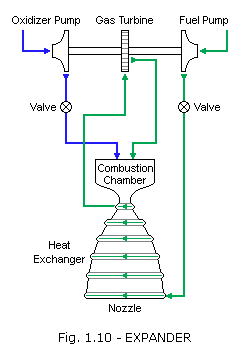
The principal modes of heat transfer to nozzle and combustor walls are convection and radiation.
Long nozzle oil can. The j 1 test stand could fire gaseous hydrogen rocket engines with up to 28000 pounds of thrust. A technician inspects an experimental copper nozzle at the j 1 test rig to study the heat transfer characteristics of nuclear rocket nozzles 6111962. A method is presented for computing the effective absorption and scattering coefficients.
I sp b creating great difficulties in the design of hot side structures that have to survive heat fluxes in the 107810 wm2 range. This tends to be a 1 3 effect on only and is therefore secondary. Less frequently these tools are used for calculating the temperatures in supersonic exhaust nozzles such as those in rockets or thrusters.
The engines were fired horizontally out of the building 1962. The results of an experimental investigation of convective heat transfer from turbulent boundary layers accelerated under the influence of large pressure gradients in a cooled convergent divergent nozzle are presented. Heat transfer in rocket nozzles general heat transfer to walls can affect a rocket in at least two ways.
The amount of heat that can flow into the coolant is controlled by many factors including the temperature difference between the chamber and the coolant the heat transfer coefficient the thermal conductivity of the chamber wall the velocity in the coolant channels and the velocity of the gas flow in the chamber or the nozzle. The investigation covered a range of stagnation pressures from 30 to 250 psia stagnation temperatures from 10300 to 20000r and nozzle inlet boundary layer thicknesses between 5 and 25 per cent of the inlet radius. A reducing the performance.
Adiabatic meaning there is no heat transfer out of or into the control volume. Heat transfer to a solid propellant rocket motor nozzle by e. A comparison of experimental heat transfer coefficients in a nozzle with analytical predictions from bartzs methods for various combustion chamber pressures in a solid propellant rocket motor comparison of solid propellant nozzle heat transfer coefficients with predicted data.
Rocket plume heat transfer thermal desktop is commonly used for thermal analyses of spacecraft and propulsion systems. Ungar i introduction the performance of a nozzle structure during a solid propellant rocket motor firing is intimately related to the heat transfer from the hot exhaust products to the nozzle surface. The temperature of the nozzle wall is an important aspect of rocket design.
At constant energy meaning no external work for example by a compressor is done on the fluid. Modern high energy solid propellants contain.